| Operation Jackpot | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Bangladesh Liberation War | |||||||
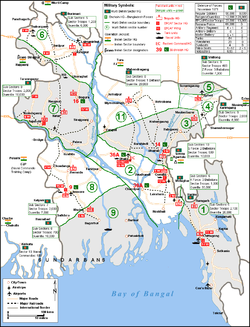 Map of Operation Jackpot, Indian Supply network for Mukti Bahini. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
(Mukti Bahinis, Sector 10) |
| ||||||
|
(CO, Z Force Brigade) (CO, K Force Brigade) (CO, K Force Brigade) * Major A.T.M Haider * Major C. R. Dutta * Major Mir Shawkat Ali | |||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
|
East Pakistan Civil Armed Force
| ||||||
Operation Jackpot was a codename for three operations undertaken by the Bengali Mukti Bahini in former East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) against the Federation of Pakistan at the climax of the Bangladesh Liberation War.[3][5]
After the Pakistani Army drove the Bengali resistance across the Indian border at the conclusion of Operation Searchlight, the Indian Army implemented a supply and training operation for the Mukti Bahini from 15 May 1971, with the goal of sending an ever increasing number of trained fighters to attack Pakistani forces and sabotage military and economic assets to demoralize Pakistani soldiers and disrupt their supply network. This enterprise was dubbed "Operation Jackpot".
Mukti Bahini Naval Commandos launched several sabotage efforts in the cities of Chittagong, Chandpur, Mongla, and the Narayanganj District against the operating combined forces of the Pakistan Soldiers, Pakistan Marines, Pakistan Navy SEAL Teams, and the East Pakistan Security Forces on the night of 15 August 1971.[3][5] Bengali submariners who had defected from Pakistani submarine PNS Mangro (S133), then based in Toulon, France, led the attacks, and this is also known as part of Operation Jackpot.[6] The Pakistani military initiated countermeasures to improve security by increasing door-to-door clearance and applied counterinsurgency tactics by the Army Special Forces and the Navy SEAL Teams, but this failed to suppress Mukti Bahini activity.[7]
The third operation was designed by Lt. Gen Sagat Singh, commander of the Indian Army IV Corps, attached to the Eastern Command, and the Bangladesh forces operating in his operational area. These forces fought against the Pakistani forces in Sylhet, Comilla, and Chittagong as part of the overall campaign from 21 November to 16 December 1971.[7]
- ^ Islam 2006, p. 211
- ^ "War in the waters: Looking back at Operation Jackpot, 1971". The Daily Star. 6 April 2023.
- ^ a b c d Jacob 2003, p. 90
- ^ Jacob 2003, p. 190
- ^ a b "Operation Jackpot". Banglapedia. Retrieved 27 July 2015.
- ^ Islam 2006, p. 265
- ^ a b Safiullah 2005, p. 211
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
